Clinical Trials
Well-characterized and manageable safety profile1-8
Toxicities are managed per established guidance9,10*
- The safety profile of CAR T therapies is well characterized, with no new unexpected serious adverse events or neurologic toxicities found in long-term follow-ups1,2,11
- After CAR T therapy, most delayed hematological toxicities improved a few months after treatment12
- Primary toxicities associated with CAR T therapy include CRS and neurologic toxicities9
- CRS is considered an “on-target” side effect of CAR T therapy13
- Often, CRS and neurologic toxicities were low, Grade 1 or 2. However, severe reactions have occurred in some patients receiving CAR T1,2,14
- Most CRS and neurologic toxicities occur within the first few weeks and are treated at the CAR T treatment center. Patients are monitored for any signs or symptoms for at least 4 weeks after infusion as delayed AEs may occur9,15,16
- Other common adverse events associated with CAR T include neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and LFT elevations12,17
The management of therapy-related toxicities has evolved with processes and strategies in place to address potential adverse events that may arise.18,19
Safety PROFILE OF CAR T THERAPY IN CLINICAL TRIALS†
| Any grade | LBCL20 | FL7,21 | ALL2 | MM22,23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRS | 78% | 49-78% | 82% | 76% |
| Neurotoxicity | 41% | 37-56% | 29% | 10.5% |
| Grade ≥3 | LBCL1,20 | FL7,21 | ALL2 | MM22 |
| CRS | 6-18% | 0-6% | 26% | 11% |
| Neurotoxicity | 16-19% | 3-15% | 12% | 8% |
| Any grade | ||
|---|---|---|
| CRS | Neurotoxicity | |
| LBCL20 | 78% | 41% |
| FL7,21 | 49-78% | 37-56% |
| ALL2 | 82% | 29% |
| MM22,23 | 76% | 10.5% |
| Grade ≥3 | ||
| CRS | Neurotoxicity | |
| LBCL1,20 | 6-18% | 16-19% |
| FL7,21 | 0-6% | 3-15% |
| ALL2 | 26% | 12% |
| MM22 | 11% | 8% |
Real-World Data
Real-world evidence improves our understanding of CAR T
SAFETY PROFILE OF CAR T THERAPY IN CLINICAL PRACTICE†
| Any grade | LBCL24-29 | ALL30 | MM31 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRS | 45-93% | 55% | 82% |
| Neurotoxicity | 15-70% | 27% | 15% |
| Grade ≥3 | LBCL24-29 | ALL30 | MM31 |
| CRS | 5-10% | 16% | 4% |
| Neurotoxicity | 1-35% | 9% | 5% |
| Any grade | ||
|---|---|---|
| CRS | Neurotoxicity | |
| LBCL24-29 | 45-93% | 15-70% |
| ALL30 | 55% | 27% |
| MM31 | 82% | 15% |
| Grade ≥3 | ||
| CRS | Neurotoxicity | |
| LBCL24-29 | 5-10% | 1-35% |
| ALL30 | 16% | 9% |
| MM31 | 4% | 5% |
AE Management
CAR T treatment centers are well equipped to manage the most common AEs: CRS and neurotoxicity9
CRS AND NEUROTOXICITY: GENERAL ONSET AND DURATION10,32,33‡
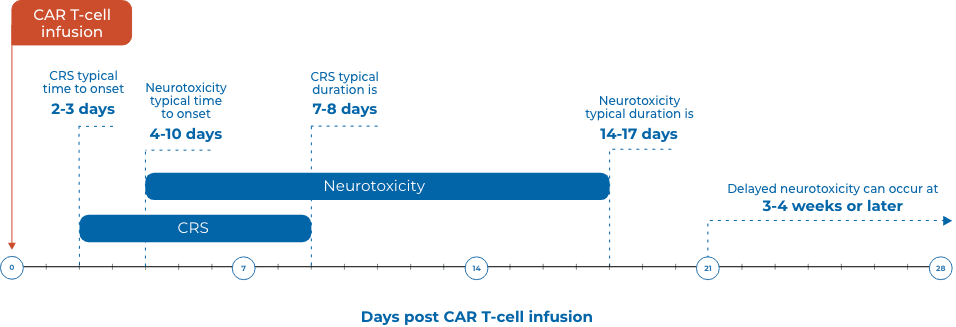
‡Presentation and duration may vary based on the individual patient and product.
| Day 1-334 | Within Week 137 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CRS | High fever is a common first sign and typically occurs before other more serious side effects19,34 | Median time to onset is 2 to 3 days and rarely later than 14 days after treatment35,36 | CRS usually occurs within the first week. Severe CRS can manifest as early as 1 day after infusion35,37,38 |
| Common signs and symptoms include: Fever, tachycardia, hypotension, depressed cardiac function, dyspnea, and hypoxia. Additional constitutional symptoms may include fatigue, headache, and myalgia.19,36,37 | |||
| Week 119 | Week 3-433 | ||
| Neurotoxicity | Can occur concurrently with high fever and other CRS symptoms, but can also occur after CRS19,33,37 | Potentially more severe symptoms can occur after CRS symptoms subside, usually more than 5 days after CAR T treatment19,33 | In ~10% of patients, delayed neurotoxicity can arise 3 to 4 weeks after treatment or later33 |
| Some of the earliest manifestations include: Tremors, dysgraphia, impaired attention, apraxia, and mild lethargy. Bradycardia, hypertension and respiratory depression, and coma can also occur.36 | |||
| CRS | |
|---|---|
| Day 1-334 | High fever is a common first sign and typically occurs before other more serious side effects19,34 |
| Median time to onset is 2 to 3 days and rarely later than 14 days after treatment35,36 | |
| Within Week 137 | CRS usually occurs within the first week. Severe CRS can manifest as early as 1 day after infusion35,37,38 |
| Common signs and symptoms include: Fever, tachycardia, hypotension, depressed cardiac function, dyspnea, and hypoxia. Additional constitutional symptoms may include fatigue, headache, and myalgia.19,36,37 | |
| Neurotoxicity | |
| Week 119 | Can occur concurrently with high fever and other CRS symptoms, but can also occur after CRS19,33,37 |
| Potentially more severe symptoms can occur after CRS symptoms subside, usually more than 5 days after CAR T treatment19,33 | |
| Week 3-437 | In ~10% of patients, delayed neurotoxicity can arise 3 to 4 weeks after treatment or later33 |
| Some of the earliest manifestations include: Tremors, dysgraphia, impaired attention, apraxia, and mild lethargy. Bradycardia, hypertension and respiratory depression, and coma can also occur.36 | |
Incidence, onset, and duration of CRS and neurotoxicity vary among individual patients and can be longer than what is listed.
Monitor for late effects of CAR T therapy
Once patients have completed CAR T therapy and are discharged from the treatment center, they return to their primary oncologist for care. Patients will enter into an observation phase that involves long-term follow-up to monitor for toxicities.9
| Potential late effects | Considerations for management§ |
|---|---|
| Cytopenia32,39(ie, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia) |
|
| Hypogamma-globulinemia32 |
|
| B-cell aplasia39,40 |
|
| Infections32,39 |
|
| Neurologic events32,39 |
|
| Secondary malignancies32 |
|
| Potential late effects |
|---|
|
Cytopenia32,39 (ie, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia) Considerations for management§
|
|
Hypogamma-globulinemia32 Considerations for management§
|
|
B-cell aplasia39,40 Considerations for management§
|
|
Infections32,39 Considerations for management§
|
|
Neurologic events32,39 Considerations for management§
|
|
Secondary malignancies32 Considerations for management§
|

*AE management may differ based on institution-specific guidance.
†Single numbers were taken from meta-analyses.
§Guidance is based on current state of evidence, expert opinion, and guideline recommendations. Institutional standards and practice may vary.32,39
AE=adverse event; ALL=acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CAR=chimeric antigen receptor; CAR T=chimeric antigen receptor T cell; CBC=complete blood count; COVID=coronavirus disease; CRS=cytokine release syndrome; FL=follicular lymphoma; IgG=immunoglobulin G; IVIG=intravenous immunoglobulin; LBCL=large B-cell lymphoma; LFT=liver function test; MM=multiple myeloma; PJP=Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
References